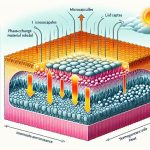
When it comes to temperature management in fabrics, understanding the roles of Phase Change Materials (PCMs) and natural thermoregulation is essential. You’ll find that PCMs actively regulate temperature through phase changes, while natural fabrics like cotton and wool rely on their inherent properties. This comparison opens up a conversation about comfort, performance, and sustainability in textiles. What implications do these differences have for your wardrobe choices and the future of fabric technology?
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs) provide active temperature regulation, dynamically responding to body heat, while natural fabrics offer passive regulation based on material properties.
- PCMs have high heat storage capacity and quick response times, whereas natural fabrics respond more slowly and have lower heat storage.
- Natural fabrics excel in moisture management, promoting comfort, while PCMs have limited moisture handling capabilities.
- PCMs typically have a shorter lifespan compared to durable natural fabrics, which generally last longer in various applications.
- Environmental impacts of PCMs include higher energy consumption and reliance on petroleum, while natural fibers are generally more biodegradable and eco-friendly.
What Are Phase Change Materials (PCMS)?
Phase Change Materials (PCMs) are innovative substances capable of absorbing and releasing thermal energy during their conversion between solid and liquid states. They play a vital role in temperature regulation, making them ideal for use in fabrics.
When temperatures rise, PCMs absorb heat and melt, keeping you cool. Conversely, when temperatures drop, they solidify and release stored heat, providing warmth. This unique property allows PCMs to maintain a comfortable microclimate against your skin, optimizing your comfort in various conditions.
You’ll find these materials in activewear, bedding, and even outdoor gear. By integrating PCMs, manufacturers enhance the functionality of textiles, making your clothing and linens not just comfortable, but also smart.
Embrace the future of fabric technology with PCMs!
The Mechanism of Natural Thermoregulation in Fabrics
Incorporating Phase Change Materials into fabrics considerably enhances their ability to regulate temperature naturally. However, natural thermoregulation in fabrics relies on their inherent properties. Fabrics like cotton and wool manage moisture and air circulation, creating a microclimate that adjusts to your body heat.
Here’s a look at how these materials work:
| Property | Function |
|---|---|
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs sweat, keeping you dry |
| Air Circulation | Promotes airflow, reducing heat |
| Insulation | Traps warmth, preventing chill |
| Breathability | Allows excess heat to escape |
| Natural Fibers | Enhances comfort and durability |
These properties contribute to a comfortable experience, allowing you to stay cool or warm as needed without relying solely on technology.
Key Differences Between PCM and Natural Fabrics
When comparing PCM fabrics to natural fabrics, you’ll notice key differences in how they regulate temperature.
PCM offers active regulation by absorbing and releasing heat, while natural fabrics rely on passive mechanisms.
This leads to distinct temperature responses that can greatly impact your comfort.
Active vs. Passive Regulation
While both phase change materials (PCMs) and natural fabrics aim to regulate temperature, they do so in fundamentally different ways.
PCMs provide active regulation by absorbing, storing, and releasing heat as they change from solid to liquid and vice versa. This means they can respond dynamically to temperature fluctuations, keeping you comfortable during varying conditions.
On the other hand, natural fabrics like cotton or wool rely on passive regulation. They allow your body to breathe and wick moisture, but they don’t actively change properties based on temperature.
In essence, PCMs react to your environment, while natural fabrics simply adapt to your body’s natural heat. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right material for your comfort needs.
Temperature Response Differences
Understanding the temperature response differences between phase change materials (PCMs) and natural fabrics can greatly impact your comfort. PCMs absorb, store, and release heat, effectively regulating your body temperature. In contrast, natural fabrics, like cotton and wool, rely on breathability and moisture-wicking properties to manage temperature. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | PCM | Natural Fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Storage | High | Low |
| Temperature Regulation | Active | Passive |
| Moisture Management | Minimal | Excellent |
| Comfort Level | Variable | Generally High |
| Longevity | Moderate | High |
Temperature Regulation: Active vs. Passive Approaches
When it comes to temperature regulation in fabrics, you’ll notice two main approaches: active and passive.
Active temperature control systems can adjust to your body’s needs in real-time, while passive insulation relies on materials that naturally maintain warmth or coolness.
Understanding the response time of each method can help you choose the right fabric for your comfort.
Active Temperature Control
Active temperature control offers a dynamic solution to managing comfort in clothing, as it actively responds to changes in your body temperature and environmental conditions. This technology utilizes smart fabrics that can adapt in real-time, ensuring you stay comfortable whether you’re working out or lounging.
Here’s a quick comparison of active temperature control and traditional methods:
| Active Temperature Control | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|
| Adjusts to body temperature | Static insulation |
| Responds to environmental changes | Relies on external conditions |
| Provides personalized comfort | Offers general comfort |
With active temperature control, you’re not just wearing fabric; you’re wearing an adaptive system that keeps you feeling just right. Embrace the future of comfort in your clothing!
Passive Insulation Mechanism
While active temperature control offers impressive adaptability, passive insulation mechanisms provide a reliable alternative for maintaining comfort in various conditions.
These systems rely on the inherent properties of materials to slow down heat transfer, allowing you to stay warm in the cold and cool in the heat. By utilizing materials with low thermal conductivity, passive insulation creates a barrier that minimizes heat loss or gain.
This means you can enjoy a more consistent temperature without needing energy-intensive solutions. Fabrics designed with passive insulation also promote breathability, enhancing comfort by preventing moisture buildup.
Ultimately, choosing passive insulation allows you to embrace a more sustainable approach to temperature regulation, ensuring comfort regardless of the environment.
Response Time Comparison
You might wonder how quickly different temperature regulation methods respond to changing conditions. Understanding the response time can help you choose the right fabric for your needs.
Here’s a comparison of active and passive approaches:
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): React within minutes, absorbing and releasing heat as temperatures fluctuate.
- Natural Thermoregulation: Slower to adjust; relies on moisture management and airflow.
- Active Systems (e.g., heated garments): Offer immediate warmth but require power sources, making them less convenient.
- Traditional Insulation: Provides consistent warmth but lacks real-time response, resulting in a delayed reaction to temperature changes.
Applications of PCM Textiles in Modern Apparel
As the demand for innovative textiles grows, phase change materials (PCMs) are making significant strides in modern apparel. You’ll find these materials in various clothing options, from activewear to casual outfits, enhancing comfort and performance.
For instance, athletes benefit from PCM-infused sportswear, which regulates body temperature during intense workouts. Additionally, outdoor gear incorporating PCMs helps maintain warmth in cold conditions while preventing overheating during physical activity.
Even everyday fashion is embracing these materials, offering stylish options that adapt to your thermal needs. By integrating PCMs, brands create garments that not only look good but also respond dynamically to environmental changes, improving your overall wearing experience.
Everyday fashion now features phase change materials, combining style with thermal adaptability for an enhanced wearing experience.
As you explore new apparel, keep an eye out for these innovative textiles.
Benefits of Natural Thermoregulation in Everyday Wear
Incorporating phase change materials into everyday wear not only enhances performance but also offers significant benefits through natural thermoregulation. You’ll notice a difference in comfort and functionality, making your daily activities more enjoyable.
Here are some key advantages:
- Temperature Control: Fabrics adapt to your body heat, keeping you cool when it’s warm and warm when it’s cool.
- Moisture Management: Natural thermoregulation helps wick away sweat, ensuring you stay dry and comfortable.
- Enhanced Comfort: You’ll experience less irritation and discomfort, allowing you to focus on your tasks.
- Versatility: These fabrics are suitable for various activities, from casual wear to athletic pursuits, making them a smart choice for any wardrobe.
Embrace the benefits of natural thermoregulation and elevate your everyday wear!
Innovations in PCM Textile Technology
While the integration of phase change materials (PCMs) in textiles continues to evolve, recent innovations are pushing the boundaries of comfort and functionality.
You’ll find that new PCM formulations are becoming more efficient, allowing fabrics to better absorb, store, and release heat based on your body temperature.
Smart textiles now utilize microencapsulation techniques, where PCMs are embedded in tiny capsules, enhancing their ability to blend seamlessly with various fabrics.
Smart textiles leverage microencapsulation, embedding PCMs in tiny capsules for seamless integration with diverse fabrics.
Additionally, companies are experimenting with hybrid materials that combine PCMs with natural fibers, offering you the best of both worlds.
These advancements not only improve thermal regulation but also enhance moisture management and breathability, ensuring your clothing adapts to changing conditions, keeping you comfortable throughout the day.
Environmental Impact of PCM vs. Natural Fabrics
The advancements in phase change materials (PCMs) raise important questions about their environmental impact compared to traditional natural fabrics.
While PCMs offer innovative temperature regulation, it’s essential to evaluate their ecological footprint. Here are some factors you should keep in mind:
- Resource Extraction: PCM production often relies on petroleum-based materials, which can deplete natural resources.
- Biodegradability: Natural fabrics like cotton and wool can break down more easily, while PCMs may linger in the environment.
- Energy Consumption: The manufacturing process for PCMs can require significant energy, increasing their carbon footprint.
- Water Usage: Natural fibers typically need water for growth, but PCM production can also strain water resources during processing.
Understanding these impacts helps you make informed choices about textile sustainability.
Economic Considerations in PCM and Natural Fabric Production
When considering the economic aspects of PCM and natural fabric production, you’ll notice significant differences in production costs.
Recycling challenges also play a vital role in the overall sustainability and affordability of these materials.
Plus, understanding market demand trends can help you make informed choices about which fabrics to use.
Production Costs Comparison
Understanding the production costs associated with phase change materials (PCMs) versus traditional natural fabrics is essential for manufacturers aiming to balance innovation with affordability.
When you evaluate these costs, consider the following factors:
- Raw Material Sourcing: PCMs often require synthetic materials, which can be pricier than natural fibers.
- Manufacturing Processes: PCM production involves advanced technology that raises initial setup costs compared to simpler natural fabric processes.
- Labor Costs: Skilled labor is often necessary for PCM integration, adding to overall expenses.
- Market Demand: While PCMs may attract premium prices in niche markets, natural fabrics have broader, established consumer bases, impacting pricing strategies.
Recycling Challenges Explained
As manufacturers weigh the production costs of phase change materials (PCMs) against traditional natural fabrics, another significant factor comes into play: recycling challenges.
You’ll find that PCMs often contain synthetic components that complicate recycling processes. These materials can’t always be easily separated or repurposed, leading to increased waste and environmental concerns.
On the other hand, natural fabrics usually have a more straightforward recycling path, but their biodegradability can vary based on the fabric’s treatment and blends.
Additionally, the lack of established recycling systems for PCMs can drive up costs, making it less appealing for manufacturers focused on sustainability.
Ultimately, understanding these challenges is essential when considering the long-term economic viability of both options in the fabric industry.
Market Demand Trends
While the demand for comfortable and temperature-regulating clothing is on the rise, it’s essential to examine how market trends influence the production of phase change materials (PCMs) compared to traditional natural fabrics.
Manufacturers are adapting to consumer preferences, leading to several noticeable trends:
- Increased Awareness: Consumers are more informed about the benefits of PCMs, driving higher demand.
- Sustainability Focus: There’s a growing preference for eco-friendly materials, bolstering traditional natural fabrics.
- Technological Innovations: Advances in PCM technology are making it more accessible and cost-effective.
- Customization Options: Shoppers seek personalized solutions in textiles, prompting brands to explore both PCMs and natural fabrics.
This dynamic landscape shapes how companies prioritize their production strategies to meet evolving consumer needs.
Future Trends in Thermoregulated Textiles
With the demand for comfort and adaptability in clothing on the rise, thermoregulated textiles are set to revolutionize the fashion industry.
Thermoregulated textiles are poised to transform fashion, meeting the growing demand for comfort and adaptability in clothing.
You’ll likely see an increase in the use of phase change materials (PCMs) that actively respond to your body temperature. These innovative fabrics won’t only keep you cool in the heat but also warm in colder conditions, enhancing your overall comfort.
Sustainable practices will play a significant role, as brands aim to source eco-friendly materials while integrating advanced technology.
Expect smart textiles that can monitor your body’s temperature and adjust accordingly, leading to a more personalized wearing experience.
As the technology evolves, you’ll enjoy clothing that’s not just stylish but also smartly engineered for your lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Care for Pcm-Enhanced Fabrics?
To care for PCM-enhanced fabrics, wash them in cold water with mild detergent and avoid fabric softeners. Tumble dry on low heat or air dry to maintain their thermoregulating properties and extend their lifespan.
Are There Any Health Risks Associated With PCMS in Textiles?
You shouldn’t worry too much about health risks from PCMs in textiles. Most studies indicate they’re safe for use, but it’s always smart to check for any specific allergies or sensitivities before wearing them.
Can PCM Fabrics Be Washed and Dried Like Regular Clothes?
You can wash and dry PCM fabrics like regular clothes, but it’s best to follow the care instructions. Avoid high temperatures and harsh chemicals to maintain their effectiveness and longevity. Your garments will thank you!
How Long Do PCM Textiles Last Before Losing Effectiveness?
PCM textiles typically last around 10 to 15 washes before they start losing effectiveness. Proper care, like gentle washing and avoiding high heat, can help maintain their performance for a longer period.
What Are the Best Applications for Natural Thermoregulation Fabrics?
You’ll find natural thermoregulation fabrics excel in activewear, sleepwear, and outdoor gear. They keep you comfortable by adapting to your body temperature, making them ideal for varied climates and activities where temperature control’s essential.
- Tetron Fabric for Marine Applications: Durability and Use Cases - June 18, 2025
- Tetron Fabric for Outdoor Furniture: Weather Resistance and Care - June 18, 2025
- Tetron Fabric for Wall Coverings: Style and Application Tips - June 18, 2025